Yellowstone Grizzly Captures- Research, Conservation & Safety
Yellowstone National Park is home to one of the most iconic and closely monitored wildlife populations in the United States the grizzly bear. Capturing and tracking these massive animals is crucial for their conservation, safety, and ecological research.
Through careful monitoring, biologists can study behavior, manage human-bear interactions, and protect both bears and park visitors. Understanding Yellowstone grizzly captures provides insight into conservation efforts, wildlife management, and the delicate balance of one of America’s most treasured ecosystems.
Yellowstone Grizzly Bear Captures: Scientific Research, Conservation, and Visitor Safety explore wildlife research, bear conservation efforts, and safety awareness for park visitors.
What Is Yellowstone Grizzly Bear Captures?
Grizzly bear capture operations in Yellowstone are scientific research activities that temporarily capture bears to gather data vital for conservation. These operations are non-lethal, and the bears are released back into their natural habitat after researchers’ complete data collection. Unlike hunting or relocation, this process focuses entirely on research and ecological management.
The Interagency Grizzly Bear Study Team (IGBST), a collaboration between the National Park Service, the U.S. Geological Survey, and other conservation agencies, oversees these operations to maintain population health and genetic diversity. Data collected from captures informs policy decisions, habitat management, and public safety measures.
Objectives of the Captures
- Assess population size, growth, and distribution
- Evaluate individual bear health and genetics
- Monitor movements, territory use, and ecological patterns
- Inform long-term conservation strategies and wildlife management
- Reduce human-bear conflicts by understanding bear behavior

These research captures ensure that Yellowstone’s grizzly population continues to recover from past declines and thrive in the modern ecosystem.
History of Grizzly Conservation in Yellowstone
Grizzly bears historically roamed much of North America, but by the mid-20th century, their numbers in Yellowstone had drastically declined due to habitat loss, hunting, and human-wildlife conflict. In the 1970s, grizzly bears were listed under the Endangered Species Act, and focused conservation efforts began.
Annual capture operations began as part of a long-term monitoring program to track population recovery and understand the factors affecting survival. These operations allow biologists to gather consistent data over decades, providing a comprehensive picture of the health and growth of the Yellowstone grizzly population.
Today, Yellowstone’s grizzly population is one of the most studied large carnivore populations in the world, and ongoing capture research has become an indispensable tool in wildlife management.
How Are Grizzly Bears Captured?
Capturing a grizzly bear is a carefully planned scientific process, designed to ensure minimal stress for the animal and maximum safety for researchers.
Baiting and Trap Placement
Biologists use natural food sources, such as road-killed elk or deer, to attract bears to a specific location. The food is placed in strategic spots where bear activity has been previously documented.
Traps, usually culvert traps or foot snares, are then placed in these areas. These devices are specially designed to safely contain the bear until researchers arrive, preventing injury and stress.
Sedation and Monitoring
Once a bear enters the trap, it is sedated using safe veterinary-approved medications. Sedation is carefully monitored by trained personnel to ensure the bear’s health remains stable throughout the procedure.
While the bear is sedated, scientists perform several tasks:
- Recording weight and measurements
- Collecting blood, hair, and tissue samples
- Fitting GPS collars or radio transmitters to track movement
- Conducting a general health assessment
This data provides critical insights into bear genetics, diet, reproduction, and ecological behavior.
Release and Recovery
After all procedures are complete, bears are carefully monitored during recovery from sedation and released at the same site. Researchers ensure the bear has fully regained mobility before leaving the area.
This process prioritizes animal welfare while allowing biologists to collect valuable long-term research data that contributes to conservation success.
Timing of Grizzly Bear Captures
Grizzly bear captures are usually conducted from late summer through early fall, typically between September and mid-October.
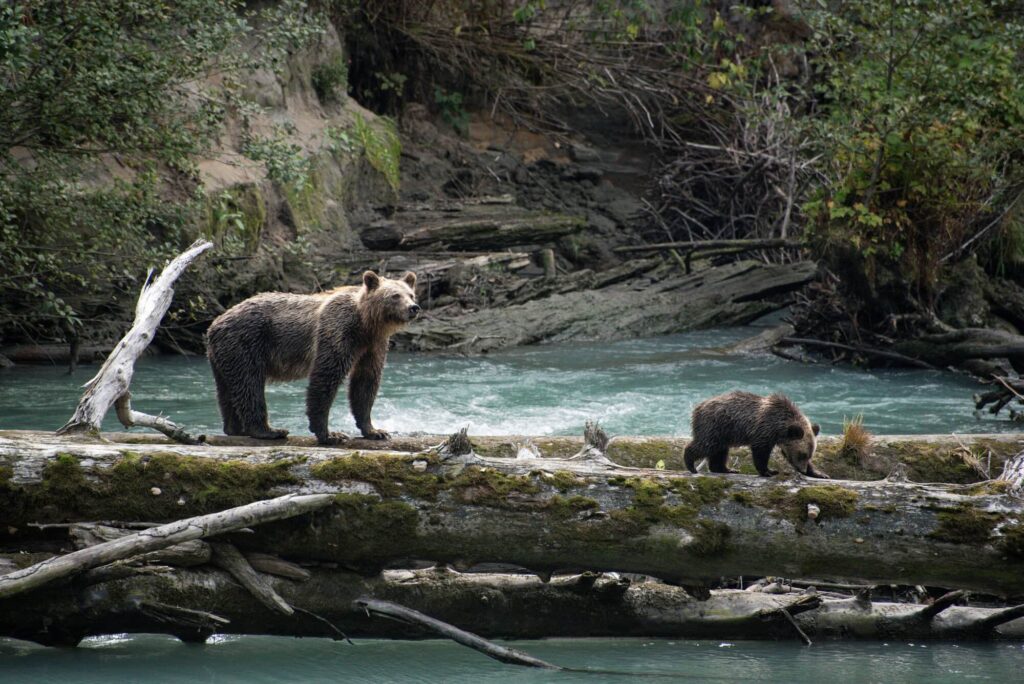

Why Autumn is Chosen
During this period, bears are actively feeding in preparation for hibernation, which makes it easier for researchers to locate and study them. Additionally, their increased movement patterns during this time provide scientists with more data on home ranges and territorial behavior.
Seasonal Planning
Each year, researchers plan capture operations months in advance, analyzing bear movement patterns, habitat use, and previous capture histories to ensure the process is safe and effective.
Agencies and Experts Involved
The Interagency Grizzly Bear Study Team (IGBST) coordinates all research captures. Team members include:
- Wildlife biologists from the National Park Service (NPS)
- Specialists from the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS)
- Conservation partners and university researchers
These professionals are trained in wildlife handling, sedation, and data collection techniques. Their expertise ensures that every capture adheres to federal animal welfare guidelines and supports long-term conservation goals.
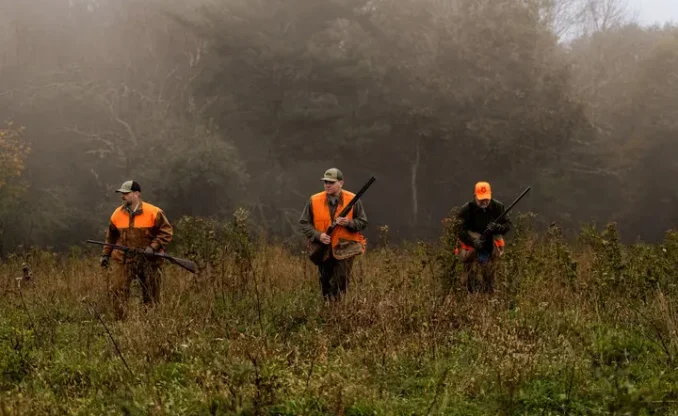
Visitor Safety During Capture Operations
Visitors to Yellowstone may occasionally see research activity during capture seasons. Safety is a top priority, and the park takes several precautions to protect both humans and bears.

Posted Warnings and Restricted Areas
- Areas with traps or bait stations are clearly marked with signs.
- Visitors are advised to avoid entering these zones.
- Rangers may temporarily restrict access to certain trails or roads.
Guidelines for Safe Wildlife Viewing
- Maintain at least 100 yards distance from bears
- Never attempt to approach a sedated bear
- Use binoculars or long lenses for observation
- Carry bear spray and know how to use it
Compliance with these guidelines ensures that both visitors and wildlife remain safe during research operations.
Conservation Impact of Capture Research
Population Monitoring
Grizzly bear captures allow scientists to track population growth and distribution, which is vital for ongoing conservation planning. Historical data shows that Yellowstone’s grizzly population has rebounded from hundreds in the 1970s to over 1,000 today.
Health and Genetics
Captured bears provide blood and tissue samples that help monitor genetic diversity and detect diseases. Maintaining healthy genetics ensures the population can adapt to environmental changes and survive long-term.
Behavioral Insights
Collars and GPS trackers allow biologists to study territorial ranges, mating patterns, and feeding habits. This information helps reduce human-bear conflicts by predicting potential bear movement near populated areas.
Common Misconceptions
Many visitors have misconceptions about Yellowstone grizzly bear captures.
- Misconception: Bears are being hunted or relocated.
Fact: Captures are strictly for research and conservation. - Misconception: The bears are in danger during capture.
Fact: Bears are handled with care, sedated safely, and released after monitoring. - Misconception: Capture operations are random or uncontrolled.
Fact: Every operation is carefully planned, with maps, timing, and safety measures.
Educating the public helps ensure cooperation and enhances overall conservation success.
Human-Bear Conflict Management
Grizzly bears sometimes interact with humans, particularly near campsites or roads. Research from capture operations informs conflict mitigation strategies, including:

- Public education campaigns
- Waste management and secure food storage
- Guidelines for campers and hikers
- Non-lethal deterrents in problem areas
These strategies reduce incidents of injury and property damage while protecting both humans and bears.
Technological Advancements in Bear Research
Modern capture research integrates technology to enhance data collection:
- GPS collars provide real-time tracking of bear movements
- Camera traps document behavior without human interference
- Remote sensors monitor environmental conditions and bear activity
These tools complement traditional capture methods, allowing researchers to gather more detailed data with minimal disruption to bears.
The Role of the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem
Yellowstone grizzly bears are part of a larger ecosystem that includes wolves, elk, bison, and diverse plant life. Capturing and studying grizzlies contributes to broader ecological knowledge:
- Understanding predator-prey relationships
- Evaluating habitat health and biodiversity
- Supporting ecosystem-wide conservation policies
Grizzly bears are keystone species, meaning their health impacts many other species in Yellowstone.
Educational and Research Benefits
Grizzly bear captures provide opportunities for:
- Student and university research on wildlife biology
- Training wildlife professionals in ethical capture techniques
- Public education about bear ecology and conservation
These benefits extend beyond Yellowstone, influencing conservation strategies worldwide.
Challenges in Grizzly Capture Operations
While essential, capture research comes with challenges:
- Difficult terrain and remote locations
- Unpredictable bear behavior
- Weather conditions affecting safety and data collection
- Balancing public access with research activities
Despite these challenges, rigorous planning and experienced teams ensure high success and safety rates.
Future of Grizzly Research
Grizzly bear research in Yellowstone is evolving. Future directions include:

- Expanding the use of non-invasive monitoring
- Long-term studies on climate change impacts
- Advanced genetic analysis for population management
- Integration with national and global conservation databases
Ongoing research ensures Yellowstone grizzlies thrive in changing environments.
Visitor Tips for Grizzly Awareness
Visitors can enjoy Yellowstone safely while supporting conservation:
- Follow posted signs and ranger instructions
- Stay on trails and designated viewing areas
- Never feed wildlife
- Learn about bear behavior through visitor centers and educational programs
- Report any unusual bear activity to park authorities
Awareness and preparedness enhance both visitor experience and wildlife protection.
FAQs
1. Why Are Grizzly Bears Captured in Yellowstone?
Bears are captured for scientific research, population monitoring, health checks, and conservation. These operations are safe, non-lethal, and help ensure long-term survival.
2. Are the Bears Harmed During Captures?
No. Bears are sedated safely, monitored by experts, and released. Procedures follow strict wildlife safety and welfare protocols to minimize stress or injury.
3. When Do Capture Operations Occur?
Operations happen late summer to mid-October, before hibernation. This timing ensures researchers can safely locate and study active bears in their natural habitat.
4. Can Visitors Enter Capture Areas?
No. Capture zones are restricted and marked. Visitors must stay clear for safety, protecting both themselves and the wildlife during research operations.
5. How Does This Research Help Conservation?
Data from captures tracks population health, genetics, and behavior, guiding conservation strategies, reducing conflicts, and supporting Yellowstone grizzly survival.
Conclusion
Yellowstone grizzly bear captures are a vital tool in wildlife conservation and ecosystem management. Conducted safely and scientifically, these operations provide invaluable insights into population health, genetics, and behavior. Visitors benefit by learning about grizzly ecology and observing from safe distances. Such research ensures Yellowstone’s grizzlies continue to thrive, maintaining the park’s ecological balance and preserving this iconic species for generations.






